GUIDETo RARE ENDOCRINE DISEASES
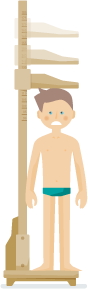
This is your illustrated guide to rare endocrine diseases
expertised by the health professionals members of FIRENDO Rare Endocrine Diseases Network
Click on the organ pictograms in white areas
in order to visualize rare endocrine and gynaecological diseases linked to this particular organ or feature.
In time, you will be able to click on every rare condition in the list,
redirecting you to a complete descrpition and all available resources on this disease.
 GROWTHMore information
GROWTHMore information
Rare endocrine growth disorders are pathologies that affect the secretion or action of the main hormones involved in growth and / or sexual development:
- Syndrome Silver Russell
- Syndrome Beckwith Wiedmann
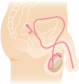
 MALE GENITAL
MALE GENITAL
ORGANSMore information
The male genital system is composed of the testes which are the male gonads, the scrotum, the various ducts, the seminal vesicles, the prostate, the urethra and the penis.
Its development can be affected by a disease of hormonal origin. Other rare endocrine disorders can affect the endocrine function of the testes more specifically.
A
- Agénésie cellules de leydig
- Anomalie du développement sexuel idiopathique 46 XX
- Anomalie du développement sexuel idiopathique 46 XY
- Anomalie du développement sexuel 46, XY par déficit en 17-bêta- déshydrogénase 3
- Anomalie du développement sexuel testicular 46 XX
- Anomalie du développement sexuel ovotesticular
- Anorchidie congénitale
B
- Bloc hormonosynthèse testiculaire
D
- Dysgénesie gonadique XY
- Dysgénesie gonadique XY/XO
E
- Exstrophie vésicale-épispadias
R
- Résistance complète aux androgènes
- Résistance partielle aux androgènes
- Résistance testiculaire gonadotrophines
S
- Syndrome de Klinefelter 47,XXY
- Syndrome de Mac Cune Albright
- Syndrome de persistance canaux Muller
T
- Testotoxicose
 THYROIDMore information
THYROIDMore information
Thyroid hormones are essential for normal physical and mental development, during childhood. In adults, they control the various metabolic systems used by the body to maintain vital functions.
Voici les maladies rares de la thyroïde que les experts de la filière FIRENDO prennent en charge :
- Hyperthyroïdie gestationnelle (familiale)
- Hyperthyroïdie non auto-immune (TSH-R)
- Hypothyroïdie congénitale avec la glande en place (avec ou sans goitre)
- Hypothyroïdie congénitale avec une anomalie de développement de la thyroïde
- Maladie de Basedow à début pédiatrique
- Résistance aux hormones thyroïdiennes
- Syndrome de Pendred
 PITUITARYMore information
PITUITARYMore information
The pituitary gland is sometimes called the "master" gland of the endocrine system because it controls the functions of many of the other endocrine glands.
The functioning of the pituitary gland can be affected by the following rare diseases:
A
- Acromégalie
- Adénohypophysite
- Adénome à prolactine
- Adénome gonadotrope
- Adénome hypophysaire mixte GH+PRL
- Adénome hypophysaire non fonctionnel
- Adénome thyréotrope
- Apoplexie hypophysaire
C
- Craniopharyngiome
D
- Déficit isolé congénital ACTH
- Déficit isolé congénital FSH
- Déficit isolé congénital TSH
- Déficit tardif isolé en ACTH
- Diabète insipide central acquis
- Diabète insipide central héréditaire
- Dysplasie septo-optique
G
- Germinome
H
- Hypogonadisme hypogonadotrope congénital
I
- Insuffisance antéphypophysaire non acquise multiple (sans PHE)
- Insuffisance hypophysaire acquise (iatrogène, trauma, Rx)
- Insuffisance hypophysaire acquise (tumeurs)
- Insuffisance hypophysaire infiltrative (histiocytose, sarcoidose, beta-thalassémie)
- Insuffisance somatotrope non acquise isolée (sans PHE)
K
- Kyste de la poche de Rathke
M
- Maladie de Cushing
P
- Panhypophysite
- Posthypophyse ectopique (PHE)
S
- Syndrome de Nelson
- Syndrome David
- Syndrome de De Morsier
 BREAST
BREAST
The breasts can also be affected by rare diseases:
- Adénofibrome géant du sein
- Malformation mammaire rare
- Polyadénomatose mammaire
- Tumeur phyllode
 ENDOCRINE PANCREASMore information
ENDOCRINE PANCREASMore information
The most important hormone that the pancreas produces is insulin. Its role is to lower glucose levels in the bloodstream and promote the storage of glucose in fat, muscle, liver and other body tissues.
The pancreas can also be affected by rare diseases (coming soon).
 ADRENALMore information
ADRENALMore information
They are mainly responsible for the management of stressful situations and hydro-mineral homeostasis.
Here are the rare adrenal diseases treated by FIRENDO experts:
A
- Adénome de Conn
C
- Complexe de Carney
D
- Déficit isolé familial en glucocorticoïdes
- Dysplasie micronodulaire pigmentée des surrénales
H
- Hyperaldostéronisme primaire
- Hyperplasie congénitale des surrénales : déficit 21 hydroxylase classique
- Hyperplasie congénitale des surrénales : déficit 21 hydroxylase non classique
- Hyperplasie macronodulaire surrénales indépendante de l'ACTH
- Hypoplasie / Hyperplasie congénitale des surrénale hors 21 hydroxylase
I
- Insuffisance surrénalienne héréditaire isolée
M
- Maladie d'Addison
P
- Paragangliome
- Phéochromocytome
- Pseudohyperaldostéronisme
- Pseudohypoaldostéronisme
R
- Résistance aux glucocorticoïdes
S
- Syndrome de Carney-Stratakis
- Syndrome de Cushing
- Syndrome de Cushing ectopique
T
- Triade de Carney
 FEMALE GENITAL
FEMALE GENITAL
ORGANSMore information
The female reproductive system has two ovaries which are the female gonads, the uterus, the vagina and the vulva. The ovary is an endocrine gland that secretes sex hormones like estrogen and progesterone. They will all have a major role in the appearance of sexual characteristics at the time of puberty, as well as for reproduction function.
The organs of the female reproductive system can be affected by the following rare diseases:
A
- Agénésie cellules de leydig
- Anomalie du développement sexuel 46, XY par déficit en 17-bêta- déshydrogénase 3
- Anomalie du développement sexuel ovotesticular
- Anomalie du développement sexuel testicular 46 XX
- Anomalie du développement sexuel idiopathique 46 XX
- Anomalie du développement sexuel idiopathique 46 XY
B
- Bloc hormonosynthèse testiculaire
D
- Déficit en aromatase
- Dysgénesie gonadique XY
- Dysgénesie gonadique XY/XO
E
- Exstrophie vésicale-épispadias
I
- Insuffisance ovarienne primitive prématurée
M
- Maladie de Von Willebrand
- Maladie hémorragique rare par anomalie des plaquettes
- Maladie hémorragique rare par déficit constitutionnel en facteurs de coagulation
- Malformations utéro-vaginales rares
P
- Pathologie utéro-vaginale ou vulvu-vaginale autre que malformative
R
- Résistance complète aux androgènes
- Résistance partielle aux androgènes
- Résistance testiculaire gonadotrophines
S
- Syndrome de Mac Cune Albright
- Syndrome de Mayer-Rokitansky-Küster-Hauser
- Syndrome de Turner
U
- Utérus bicorne
- Utérus cloisonné
- Utérus double - hémivagin - agénésie rénale
V
- Vagin cloisonné

